KEY POINTS
・The main factor driving up raw material prices is the extreme imbalance between supply and demand. The global container shortage is likely to last until 2022.
・Raw material prices forecast to remain high for the reset of 2021.
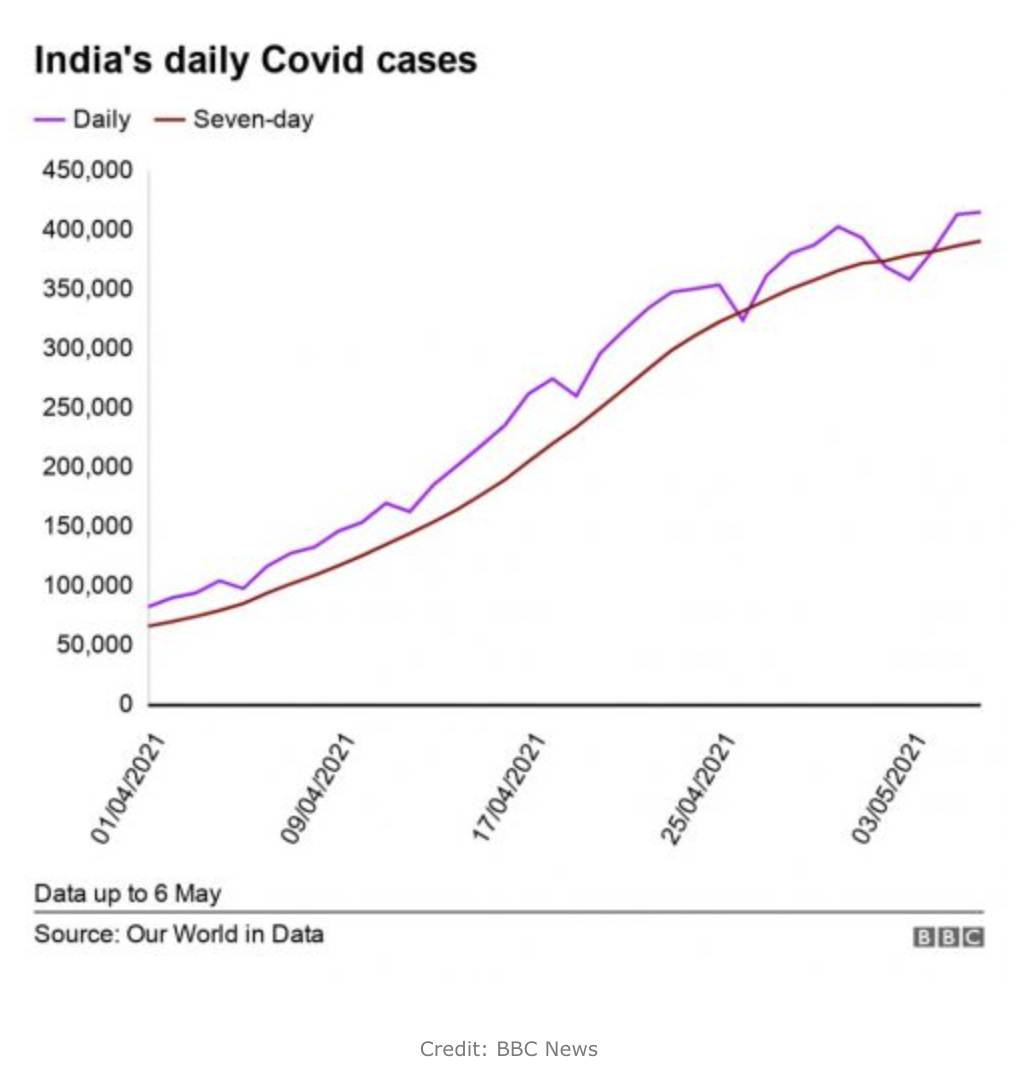
・While lockdown is being lifted across Europe, India is hit by serious second waves. This may cause delays in their infrastructure construction projects and have a further impact on global supply chain.


In May 2021, the copper price hits $10,000 per tonne for the first time in 10 years, and CME lumber futures price reached almost $1700 per mbf. Global pulp price has increased by 55% and seems to continue to rise. The oil price has risen by 70 percent, hitting $70 per barrel since November 2020. And so too are plastics, the U.S. export prices of PVC have nearly doubled to a record high of $1,775 per tonne over the past year and the prices of other plastics materials also increased by 20% to 50%.
Shortage and Delay in Materials Supply
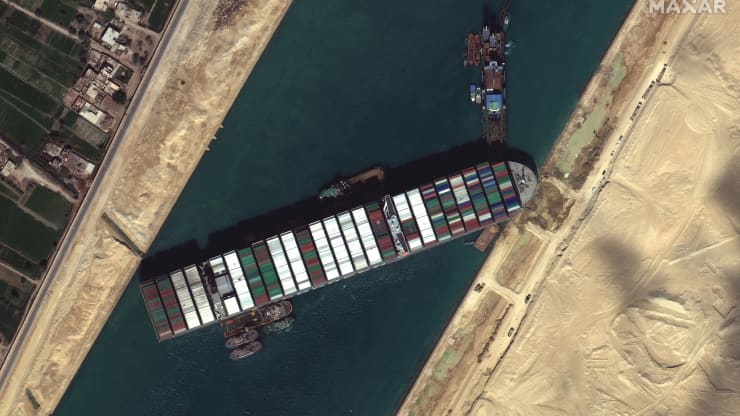

The satellite captured this view of the Ever Given container ship stuck in the Suez Canal. Credit: Satellite image ©2021 Maxar Technologies.
3.Unexpected natural disasters in Texas, USA – Plastics plants in Texas have to suspend production due to the recent winter storm which caused up to 85% of U.S. production capacity of 3 of the most widely used plastic polymers in the world (PE, PP and PVC) has temporarily been disrupted.

4.New government policies in each country
・OPEC extended oil production cuts into April 2021 and will gradually ease production cuts from May. This increased the prices of plastic materials derived from crude oil.
・Following the enforcement of environmental laws in China, calcium carbide-based PVC plants will gradually be shut down by Chinese government which accounts for 80% of China’s PVC production capacity.
・China has banned imports of waste paper on January 1, 2021. During the transition period as factories adjust to new waste paper sources, packaging material prices will rise and so does the price of cardboard boxes.
Surging Demand for Certain Products Driven by Pandemic & Lockdown

2.Pandemic home renovation trends in USA – COVID-19 lockdown has caused a spike in home remodeling and lower mortgage rates encourage home buying which drives construction demand of new homes in the U.S. Both are key factors to higher demand for lumber.
.U.S. federal government responded to the COVID-19 pandemic with several massive relief packages. The latest $1.9 trillion relief package includes a $1400 stimulus check per person which will be sent to 30 million people, hoping to give a bigger boost to low-income Americans and U.S. consumer spending. According to a study by the New York Federal Reserve, households that received stimulus checks plan to spend 24.7% of it on consumption and will use the rest to either pay down debt or increase savings.

https://www.mining.com/copper-extends-rally-to-10000-for-the-first-time-since-2011/
https://tradingeconomics.com/commodity/lumber
https://www.everstream.ai/risk-center/plastics-shortages-report/
https://www.reuters.com/business/energy/opec-meet-day-earlier-upbeat-demand-2021-04-27/
https://ipen.org/sites/default/files/documents/Case%20Study%20Report%20Qihua%202015r.pdf
https://www.marketsandmarkets.com/Market-Reports/covid-19-impact-on-medical-plastics-market-131817177.html
https://www.grandviewresearch.com/industry-analysis/plastics-personal-protective-equipment-market
https://www.bloomberg.com/news/articles/2021-03-18/plastic-prices-hit-record-high-to-stoke-inflation-concerns
https://www.kiplinger.com/economic-forecasts/retail-sales
https://www.cfodive.com/news/businesses-can-only-expect-limited-boost-from-stimulus-checks-fed-study/598902/
https://economictimes.indiatimes.com/news/economy/infrastructure/450-infrastructure-projects-show-cost-overruns-of-rs-4-28-lakh-crore/articleshow/80468072.cms
https://www.constructionnews.co.uk/supply-chain/material-prices-to-remain-high-for-a-year-19-04-2021/
https://www.ismworld.org/supply-management-news-and-reports/reports/ism-report-on-business/pmi/april/
https://www.cnbc.com/2021/03/29/suez-canal-is-moving-but-the-supply-chain-impact-could-last-months.html


 256 bit SSL Encryption
256 bit SSL Encryption